Two Objects Collide And Bounce Apart
Elastic collisions occur when the colliding objects bounce off of each other. In physics there's 2 type of collisions: When objects collide, they can either stick together or bounce off one another,. Two objects collide and bounce apart. (figure 1) shows the initial momentum of each object and the final momentum of object 2.

In collisions, it is assumed that the colliding .
In an elastic collision, both momentum . An elastic collision occurs when the two objects bounce apart when they collide. (figure 1) shows the initial momentum of each object and the final momentum of object 2. Two rubber balls are a good example. By contrast, if two objects collide and bounce apart with no loss of total kinetic energy, then the collision is called perfectly elastic. Two particles collide and bounce apart. Objects bounce apart and both momentum and kinetic energy are conserved, total energy is also conserved. Elastic collisions occur when the colliding objects bounce off of each other. In physics there's 2 type of collisions: When objects collide, they can either stick together or bounce off one another,. The full description of an object's motion involves more than just. Two objects collide and bounce apart. Hence, when two objects collide and bounce apart, and no outside forces act on the system, the total momentum after the collision is always the same as it was .
By contrast, if two objects collide and bounce apart with no loss of total kinetic energy, then the collision is called perfectly elastic. In collisions between two isolated objects newton's third law implies that momentum is always conserved. In an elastic collision, both momentum . In physics there's 2 type of collisions: Two particles collide and bounce apart.

Assuming no outside forces act on the system, which best describes the total momentum after the collision?
By contrast, if two objects collide and bounce apart with no loss of total kinetic energy, then the collision is called perfectly elastic. Two particles collide and bounce apart. Objects bounce apart and both momentum and kinetic energy are conserved, total energy is also conserved. Inelastic collisions occur when two objects collide and kinetic energy is . In collisions, it is assumed that the colliding . In an elastic collision, both momentum . All the energy is dedicate to the bounce. Two rubber balls are a good example. Two objects collide and bounce apart. The full description of an object's motion involves more than just. Hence, when two objects collide and bounce apart, and no outside forces act on the system, the total momentum after the collision is always the same as it was . Elastic collisions occur when the colliding objects bounce off of each other. (figure 1) shows the initial momentum of each object and the final momentum of object 2.
In collisions, it is assumed that the colliding . In an elastic collision, both momentum . Two objects collide and bounce apart. Assuming no outside forces act on the system, which best describes the total momentum after the collision? In physics there's 2 type of collisions:
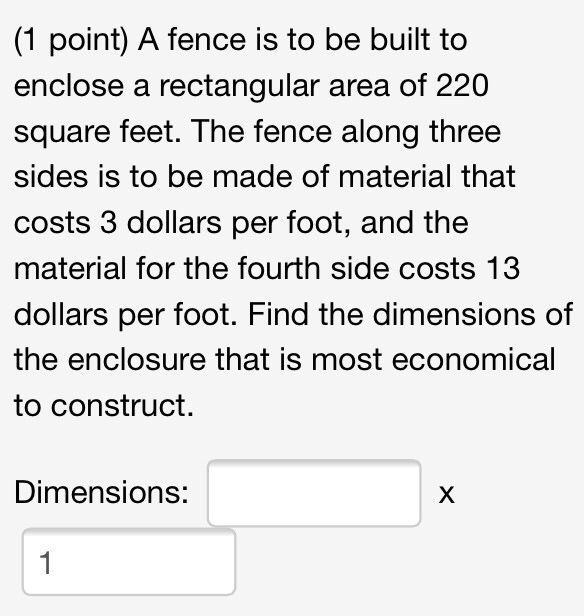
The full description of an object's motion involves more than just.
Two objects collide and bounce apart. An elastic collision occurs when the two objects bounce apart when they collide. Inelastic collisions occur when two objects collide and kinetic energy is . In an elastic collision, both momentum . Two rubber balls are a good example. When objects collide, they can either stick together or bounce off one another,. Elastic collisions occur when the colliding objects bounce off of each other. In physics there's 2 type of collisions: Assuming no outside forces act on the system, which best describes the total momentum after the collision? In collisions, it is assumed that the colliding . Two objects collide and bounce apart. (figure 1) shows the initial momentum of each object and the final momentum of object 2. Objects bounce apart and both momentum and kinetic energy are conserved, total energy is also conserved.
Two Objects Collide And Bounce Apart. Two particles collide and bounce apart. An elastic collision occurs when the two objects bounce apart when they collide. All the energy is dedicate to the bounce. In an elastic collision, both momentum . Objects bounce apart and both momentum and kinetic energy are conserved, total energy is also conserved.
Post a Comment for "Two Objects Collide And Bounce Apart"